
- Details
- Category: Blog
During an online training session, the course leader is not aware of individual progress without feedback from the learner.
 To provide that feedback, learners need to be more aware of what is expected from them at each learning step. That way they will have confidence that have correctly understood each learning point, or they can ask the course leader for help.
To provide that feedback, learners need to be more aware of what is expected from them at each learning step. That way they will have confidence that have correctly understood each learning point, or they can ask the course leader for help.
It may seem counter intuitive, but the learners first step is to identify what they want from the course. A clear learning goal is the foundation for good progress through the course learning steps because 1. It will help the course leader understand your current level of understanding2. It will help you to set realistic expectations and begin the learning process by mapping out gaps in your knowledge and 3. Help to motivate you when working through new things that don't immediately make sense.
The notes below explain the learning steps and signposts that help learners to collaborate with the course leader and get the most out of the online training experience.
A well designed online training course uses 4 learning signposts guide your journey from "awareness to competence".
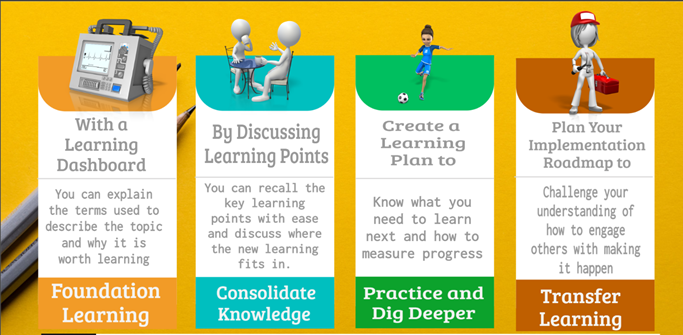
As a learner, to make the most progress your role as you approach each signpost is set out below.
Learning Step 1: Create a Learning Dashboard
- Record the topic basics and why it is worth learning as a One page learning dashboard.
- Use this to record and remember the terms that explain the basic principles and techniques.
- Make notes under these topic headings. Revise the dashboard as you learn more.
- Make sure that you complete the polls/questions contained within the course. These are designed to help you to avoid misconceptions and false learning.
- Spending just 30 seconds at the end of each section on recall (what have I learned here) vastly increases the retention of new ideas.
Learning Step 2: Discuss Key Learning Points
- Add key learning points to your dashboard.
- Develop familiarity with these and use discussions to test recall and identify gaps in understanding.
- Try to develop links between the key learning points and your learning goals.
- Use the process to highlight areas which you need to go back to or ask the course leader about.
Learning Step 3: Create Your Learning Plan
- Create a learning plan involving practical activities to systematically build capability.
- Adults learn best through practical application. Focus next on how to apply the new learning to the real world.
- Practical activities helps you to reinforce what you have learned and develop the understanding to apply those lessons to the workplace.
- Working with others on the course to review this will help you to develop confidence as well as competence.
Learning step 4: Plan Your Implementation Roadmap
- Build an implementation road map that includes activities to share lessons learned so that you can co-design the detailed approach to making it happen when you return to the workplace.
- Creating a plan to help others learn is a powerful skill development process.
- This might include:
-Working with stakeholders to agree a forward plan.
-Awareness to senior management to get approval for resources.
-Mobilising activities to try out the ideas in a pilot area.
The planning process will highlight areas you find complex or are uncertain about.
This will surface topics to share with the course leaders and others during the course action planning activity.
Finally, Take time to develop digital skills
 Assess strengths and weaknesses in the following areas. Develop a learning plan to work on weak areas.
Assess strengths and weaknesses in the following areas. Develop a learning plan to work on weak areas.
1. Communication and collaboration
Able to respond to and develop ideas in a remote environment
Able to consistently apply file naming conventions and version numbers to avoid confusion re updates.
2. Use of different devices
Able to use computer or iPad audio and webcam parameters
3. Use of Information
Able to find files, analyse information and interpret results.
4. Learning skills
Able to study and learn in technology rich environments
5. Produce materials for others to learn
Able to identify learning paths and produce material to support each step
6. Identity management/digital reputation
Able to explain core competencies and adopt supportive team protocols
7. Digital Scholarship (emerging approaches)
Able to assimilate new software functions and use productively.








